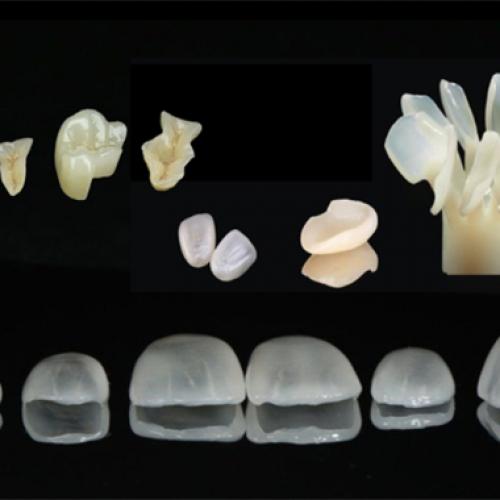
Porcelain Fused to Metal (PFM), also known as metal-ceramic restoration, is a widely used dental restoration technique.
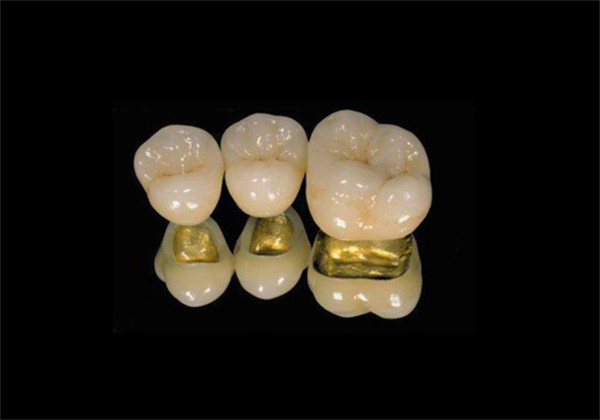
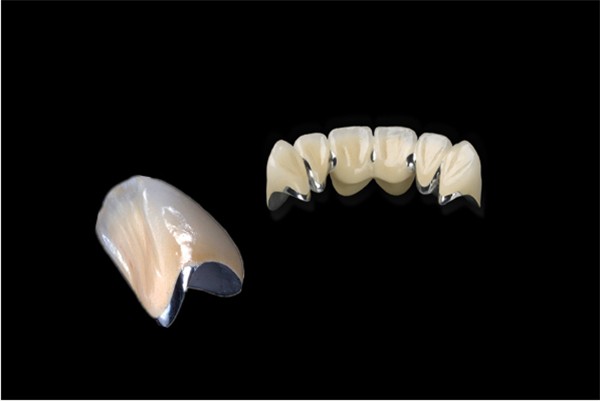
PFM combines the strength and durability of a metal substructure with the aesthetic appeal of porcelain. The metal base provides stability and support, while the porcelain layer on top gives a natural look that closely mimics the appearance of natural teeth.
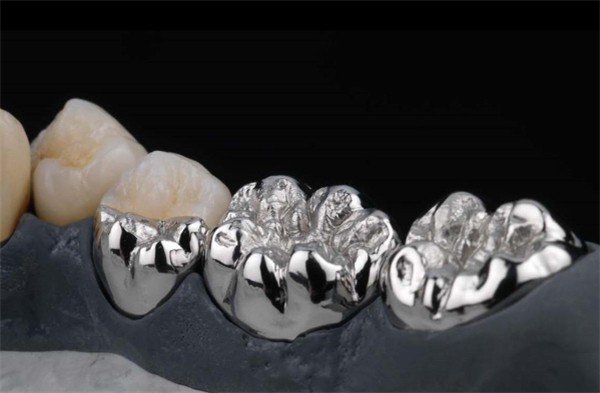
The process of creating a PFM restoration involves several steps. First, an impression of the patient's teeth is taken. Then, a metal framework is fabricated to fit precisely over the prepared tooth. This metal framework is usually made of alloys such as cobalt-chromium or nickel-chromium. Once the metal framework is ready, porcelain is fused onto it in a high-temperature furnace. The porcelain is carefully layered and shaped to achieve the desired color, translucency, and contour.
One of the main advantages of PFM restorations is their durability. The metal base makes them strong enough to withstand the forces of chewing and biting. At the same time, the porcelain layer provides an excellent aesthetic result, blending in seamlessly with the surrounding natural teeth. PFM restorations can be used for crowns, bridges, and veneers.
However, PFM restorations also have some limitations. The metal substructure can sometimes cause a grayish appearance at the gum line, especially if the patient has thin gums. In addition, the fabrication process is relatively complex and requires multiple visits to the dentist.
Overall, Porcelain Fused to Metal is a reliable and effective dental restoration option that offers a good balance between strength and aesthetics.